Resin transfer molding, or RTM, is a clean and repeatable method for producing strong composite parts with smooth A-class surfaces on both sides.
In RTM, dry fibers are pre-shaped, placed in a matched mold, and infused with low-viscosity epoxy, vinyl ester, or polyester under injection pressure, then cured.
This guide shows how the process works, how it compares to VARTM and LRTM, and what to do at every step to get reliable parts.
Quick Takeaways:
- Resin transfer molding (RTM) is a process that uses a closed mold to create composite parts.
- Dry fibers, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, are placed in a mold, and then liquid resin is injected to bond and harden them.
- It is widely used in aerospace, automotive, renewable energy, and crafting.
- Benefits include durability, lightweight design, and smooth finishes.
- Challenges include higher setup costs and longer preparation.
You May Want To Shop
|
|
Resiners® 1 gallon/2 gallon Crystal Clear Epoxy Resin with Tailored Diversion Port
This top-quality resin is perfect for coasters, jewelry, and countertops. The graduated, ergonomic bottles make measuring and handling easy. |
What Is Resin Transfer Molding?
Resin transfer molding (RTM) is a closed mold process used to create strong, lightweight composite parts.
In this method, dry reinforcement fibers are placed inside a sealed mold, and a liquid resin, such as epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester, is injected under pressure to saturate them. Once cured, the resin hardens around the fibers, forming a durable structure.
Because RTM is a closed process, it provides better surface finishes, precise part control, and reduced fumes compared to open mold methods.
It is more reliable than hand lay-up but less costly and complex than high-pressure compression molding, offering a balanced option for producing quality composites at a moderate scale.
📌Also Read: Epoxy Resin Mold Material: Best Options & Tips Explained
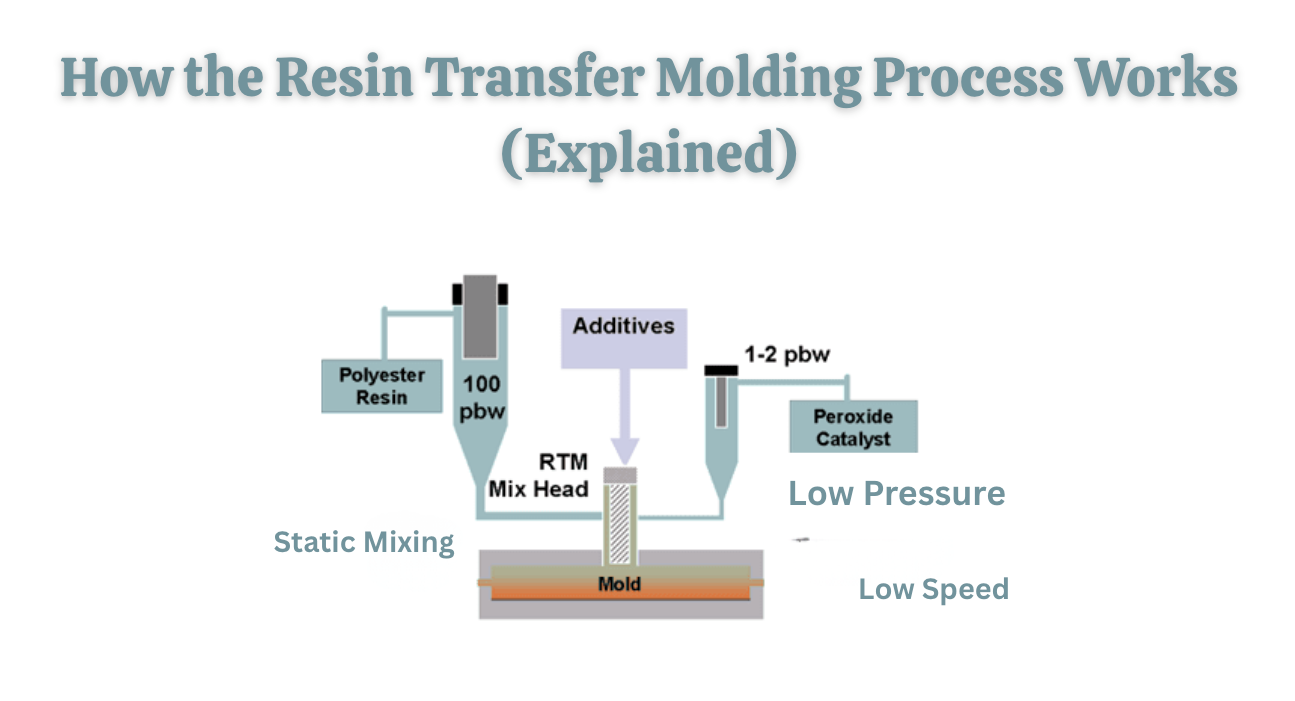
How the Resin Transfer Molding Process Works

The RTM process can be broken down into a series of steps. Each step must be done carefully to make sure the final product is strong and reliable.
Step 1: Mold Preparation
- Molds are usually made from metal like aluminum or steel, but sometimes high-strength composites are used.
- A release agent is applied to the inside of the mold, allowing the part to come out smoothly after curing.
- The two halves of the mold must line up perfectly to prevent leaks and defects.
Step 2: Fiber Reinforcement Placement
- Pre-cut fiber fabrics or mats, such as fiberglass, carbon fiber, or natural fiber reinforcements, are laid into the mold.
- Placement matters because fiber orientation controls the strength and flexibility of the finished part.
- Sometimes preforms are made to hold fibers in position before resin is added.
Step 3: Resin Injection
- The mold is sealed, and resin is injected under controlled pressure.
- Low-viscosity resins are chosen because they flow easily and fill the mold without leaving air pockets.
- The resin flows through ports and channels until all the fiber reinforcement is completely saturated.
Step 4: Curing and Solidification
- After injection, the resin is cured to harden the part.
- Curing can be done by heating the mold or using specialized curing machines that control time and temperature.
- In some small-scale crafts, UV lamps or heat guns can help with curing.
Step 5: Demolding and Post-Processing
- Once fully hardened, the mold is opened, and the part is removed.
- Extra resin flashes and rough edges are trimmed away.
- Depending on use, the part may be sanded, polished, or coated.
This process gives precision and produces parts with smooth finishes and consistent strength.
📌Also Read: 12+ Creative Summer Resin Craft Ideas for Kids and Adults
Benefits of Resin Transfer Molding
The popularity of RTM comes from the balance it offers between cost, quality, and performance.
- High strength-to-weight ratio: Ideal for aerospace and automotive industries where lightweight materials are essential.
- Smooth surface finish: RTM parts often have a glossy finish, making them ready for painting or coating with minimal additional work.
- Reduced emissions: Since it is a closed process, fewer volatile chemicals escape into the air.
- Repeatability: Each part made with RTM is nearly identical, which is valuable for manufacturing.
- Less waste: Resin is injected in controlled amounts, reducing spills and unused material.
For crafters and smaller projects, these same benefits apply on a smaller scale. The use of epoxy resin kits, heat guns, and UV light curing has opened up new creative pathways.
Challenges and Limitations
RTM is not perfect. Some challenges come with it:
- Costly tool setup: High-quality molds are expensive.
- Complex preparation: Fiber placement must be precise, and even minor mistakes can compromise the part's integrity.
- Slower cycles for small runs: Good for medium production, not great for single quick builds.
- Limited to specific thicknesses: Though flexible, RTM does not always work well for extremely thin or very intricate details.
These drawbacks mean RTM is best suited for industries where high performance and consistency justify the costs.
Applications of Resin Transfer Molding
RTM is a versatile manufacturing method with applications in different fields.
- Aerospace: aircraft panels, wings, fairings, and interior parts.
- Automotive: car hoods, fenders, roof panels, and lightweight structural elements.
- Renewable energy: wind turbine blades and clean energy components.
- Marine industry: boat hulls and deck parts requiring high durability.
- Crafting and DIY resin art: makers use scaled-down RTM ideas to create furniture parts, jewelry molds, and custom projects with curing tools.
The variety of use cases shows the broad potential of RTM for both large industries and small creative projects.
Resin Transfer Molding vs Other Resin Processes
|
Process |
Method |
Best For |
Limitations |
|
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) |
Closed mold, resin injected under pressure |
Strong, detailed medium-to-large parts |
Higher setup cost |
|
Vacuum Infusion |
Resin pulled through fibers using vacuum |
Large, low-cost builds like boats |
Slower, less precise |
|
Hand Lay-Up |
Resin manually applied to fibers |
Simple small parts and prototypes |
Inconsistent and labor-heavy |
|
Compression Molding |
Heat and pressure applied in a mold |
Mass production of composites |
Very high tooling cost |
This comparison shows how RTM is well-positioned for projects that need balance between precision and cost.
RTM vs VARTM vs LRTM
What to do: Select the route that best suits your volume, finish, and budget.
-
RTM: Two rigid mold halves. Resin is pumped in under pressure. You get two good surfaces and tight tolerances. This fits mid-volume production. Injection pressure can be far higher than vacuum, which helps fill tricky geometry.
-
VARTM, vacuum-assisted RTM: One rigid tool and a vacuum bag on top. Resin is drawn in by vacuum. Tooling is cheaper and large parts are possible, but usually only one side has an A-class surface straight off the tool.
- LRTM, light RTM: Two matched tools, but the system runs at low cavity pressure with help from vacuum. Tooling is lighter and costs less than heavy RTM. It reduces waste and emissions, and can still be consistent
Quick Pick Guide:
- Need two smooth sides, tight sizes, and repeatability. Choose RTM.
- Building very large parts with a tight budget. Choose VARTM.
- Want matched tools and lower cost with steady quality. Choose LRTM.
📌Also Read: Epoxy vs Resin: Key Differences & Best Uses Explained
Conclusion
Resin transfer molding is a proven method for creating strong, lightweight, and precise composite parts, used in a wide range of applications, from airplanes and cars to resin crafts.
By combining fibers with resin inside a closed mold, RTM delivers consistent quality and reliable performance.
Whether you’re a professional in composites or a crafter experimenting with epoxy, understanding RTM can guide better projects and inspire new ideas.
Helpful Tools For Small Shops And Makers
- Resin Curing Machines. Keep cures stable. Great for small parts and post-cures.
- Epoxy Resin. Use clear and low-viscosity systems for RTM test shots and fixtures.
- UV Lights For Curing Resin. Handy for spot fixes and small top coats.
- Heat Guns For Crafts. Chase microbubbles on edges and help flow thin coats onto cosmetic faces.
FAQs About Resin Transfer Molding
What is the difference between LRTM and RTM?
RTM injects resin into a closed mold under pressure to wet out dry fiber. LRTM, or Light RTM, uses vacuum to draw low-viscosity resin through the fibers, so injection pressures and tooling costs are lower. RTM suits higher volumes and thicker parts that need more control of flow under pressure. LRTM is great for clean shops, smoother surfaces on both sides, and medium-volume production.
What is the process of light resin transfer molding?
Place dry fabrics in a rigid mold, add peel ply or flow media if needed, and close it with a lightweight counter-mold and seals. Pull a vacuum to check for leaks, then mix the resin and open the inlet so vacuum draws resin across the part. Watch the flow front until all areas are wet, then clamp the feed and keep vacuum on while the resin gels. Let the part cure per the datasheet, then demold and trim.
What resins are commonly used in RTM?
Low-viscosity systems with long working time are preferred. Epoxy, vinyl ester, and unsaturated polyester are the most common choices. Epoxies use amine hardeners, while vinyl ester and polyester use MEKP catalyst. Pick a resin rated for RTM or infusion to reduce voids and improve wet-out.
Are RTM parts strong?
Yes. RTM often gives higher fiber content and lower voids than hand layup, which boosts strength and stiffness. Parts come out with consistent thickness and good bonding between layers. Correct cure schedules further improve heat resistance and durability.
What is resin transfer molding used for?
RTM makes medium to large composite parts with clean surfaces on both sides. Typical uses include automotive body panels, marine decks and hull sections, wind energy parts, and equipment covers. It also works for furniture, sports goods, and medical housings. The process fits runs where repeatability, low emissions, and good finish are important.












Dejar un comentario
Este sitio está protegido por hCaptcha y se aplican la Política de privacidad de hCaptcha y los Términos del servicio.