The chemical formula of epoxy might seem complicated at first, but understanding it helps explain why epoxy resin is one of the most reliable materials for crafts, construction, and industry.
Whether you are mixing epoxy for a DIY project or curious about its industrial chemistry, learning the basics makes you a smarter maker.
Quick Takeaways:
- Epoxy resins are based on molecules containing epoxide groups, which are three-membered rings with oxygen.
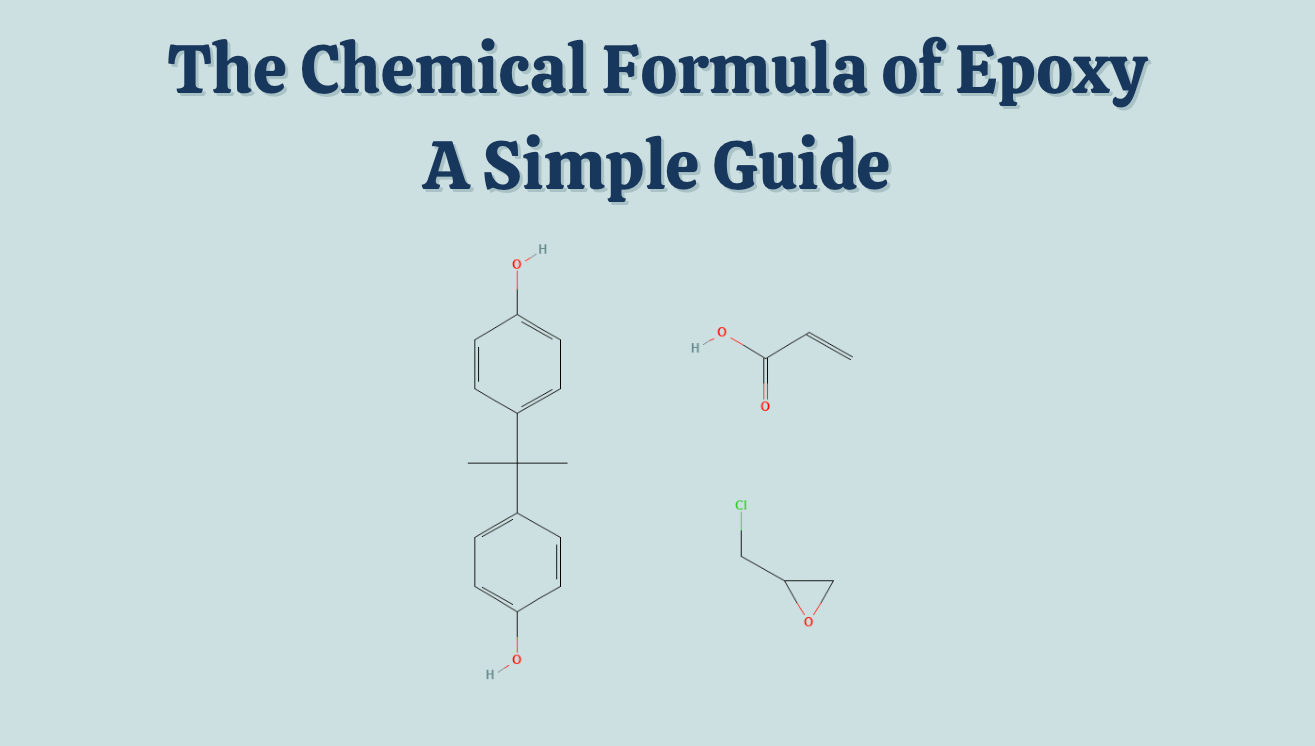
- The most common epoxy resin is DGEBA (diglycidyl ether of bisphenol-A) with the formula C21H25ClO5
- Epoxy becomes strong when mixed with a curing agent, which opens the epoxide ring and creates cross-linked polymer chains.
- This curing process explains why epoxy is durable, chemically resistant, and widely used.
- Epoxy resins are used in crafting, construction, aerospace, electronics, and more.
You May Want To Shop
|
|
Resiners® Crystal Clear Epoxy Resin with Diversion Port
This resin is perfect for all your jewelry, coasters, and tabletop projects. The ergonomic, graduated bottles make measuring easy. |
What Is Epoxy?
Epoxy is a family of resins that contain an epoxide group, giving them unique strength and durability.

Photo Source from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Epoxy-Resin
Unlike thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, epoxy is a thermosetting polymer, which means that once cured, it cannot be melted or reshaped.
You can find epoxy in many everyday uses:
- Strong adhesives for woodworking, construction, and crafts
- Protective coatings for floors, furniture, and surfaces
- Electrical encapsulants that shield sensitive electronics
- Clear casting resins for jewelry and resin art
This wide versatility comes from the powerful chemistry that defines epoxy.
📌Read More: Epoxy vs Resin: Key Differences & Best Uses Explained
The Chemical Formula of Epoxy Explained
The Epoxide Group
The key unit inside epoxy resins is the epoxide group, also known as an oxirane ring. This is a three-membered ring made up of two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Its simple chemical formula is C2H4O.
The epoxide ring is very reactive because of the strain caused by bending bonds inside the ring.
This reactivity enables the ring to open and form bonds with other molecules, which is the basis of the curing reaction in epoxy.
Common Epoxy Resin: DGEBA
The most widely used epoxy resin is DGEBA (diglycidyl ether of bisphenol-A).
- Chemical formula: C21H25ClO5
- Made from: bisphenol-A (BPA) and epichlorohydrin.
- Structure: Contains two epoxide groups at the ends, which can react with curing agents.
DGEBA is popular due to its predictable properties and ease of processing. It makes strong adhesives, coatings, and castings found in both industry and crafts.
Other Epoxy Variations
While DGEBA is the most common, other epoxy resins exist:
- Bisphenol-F epoxy resins: similar to DGEBA but lower viscosity for better flow.
- Aliphatic epoxy resins: used for UV resistance and clear finishes.
- Novolac epoxy resins: multiple epoxide groups for extra chemical resistance.
This variety demonstrates that the "epoxy formula" can be adjusted to achieve the desired properties.
✨Shop Related Products✨
How Epoxy is Cured into a Solid
Epoxy resin by itself is usually a liquid or semi-solid. It only becomes useful when mixed with a curing agent (also called a hardener).
- When the curing agent is mixed in, it reacts with the epoxide groups by opening the strained oxirane ring.
- As more epoxide rings open, they bond with curing agent molecules, creating long chains and networks.
- This process is called cross-linking. It creates a strong three-dimensional polymer structure.
Common curing agents include:
- Amines (polyamines, aliphatic or aromatic)
- Acid anhydrides
- Thiols
The result is a thermosetting polymer. Once set, it cannot be melted or reshaped. This is why cured epoxy is so tough and heat-resistant.
📌 Read More: Epoxy Resin Projects You Can DIY at Home
Why the Chemical Formula of Epoxy Matters
Understanding the chemical formula is not just for chemists; it is essential for everyone. It helps you know what epoxy is capable of and how to use it safely.
- The epoxide group explains why epoxy is reactive and cures strongly.
- Knowing the chemical basis lets you decide between BPA-based vs BPA-free epoxy resins.
- The curing agents play an important role in setting the working time and hardness of the resin.
- In crafts, this knowledge explains why mixing ratios are critical and why under- or over-curing causes failures.
Benefits of Epoxy Resins
Epoxy is popular for good reasons. Its formula and curing process create unique advantages:
- High mechanical strength: Strong bonds and cross-linked structure.
- Chemical resistance: Tolerates water, oils, and many chemicals.
- Adhesion: Bonds strongly to wood, metal, glass, and plastics.
- Thermal stability: Resistant to high heat compared to many plastics.
- Clear finish: Epoxy can create glossy, glass-like surfaces.
This explains why you see epoxy in both industrial applications and DIY crafts.
📌Read More: Polyester Resin vs Epoxy Resin: Which Should You Choose?
Challenges and Safety Considerations
Even with its strengths, epoxy has some limitations and safety issues:
- Toxicity before curing: Liquid epoxy and hardeners can irritate skin and cause allergic reactions. Always wear gloves and safety glasses.
- BPA concerns: Some epoxies made with BPA may raise health concerns, prompting the development of BPA-free alternatives.
- Handling issues: Incorrect mixing ratio often leads to sticky or incomplete curing.
- Cost: High-quality epoxies can be more expensive compared to polyester resins.
Applications of Epoxy
Epoxy is one of the most widely used materials in the modern world.
- Aerospace and automotive: Lightweight composite parts, adhesives, coatings.
- Construction: Floor coatings, strong glues, reinforcement for concrete.
- Electronics: Protecting wires, sealing circuit boards, and insulation.
- Marine: Boat repairs, protection against water damage.
- DIY and art: Furniture finishing, jewelry, river tables, and custom art pieces.
What makes epoxy unique is that the same chemistry that serves engineers in aerospace also works for hobbyists at the craft table.
Comparing Epoxy to Other Resins
|
Resin Type |
Formula Base |
Uses |
Strengths |
Limitations |
|
Epoxy |
Epoxide group, varies (DGEBA common) |
Adhesives, coatings, crafts, composites |
Strong, durable, chemical resistant |
Needs curing, more expensive |
|
Polyester |
Unsaturated polyesters |
Boats, auto parts, large-scale projects |
Inexpensive, cures quickly |
Brittle, lower durability |
|
Polyurethane |
Isocyanates and polyols |
Foams, coatings, elastomers |
Flexible, versatile |
Sensitive to moisture during cure |
|
Vinyl Ester |
Vinyl groups with reactive ends |
Marine and chemical-resistant parts |
Strong, corrosion-resistant |
More costly than polyester |
Conclusion
The chemical formula of epoxy explains why it is so valuable in both industry and crafts.
Its epoxide group, once cured with hardeners, creates a tough and versatile thermosetting polymer.
When mixed correctly and handled with care, epoxy provides reliable performance for engineers, builders, and hobbyists.
If you are ready to explore epoxy in your own projects, check out these hand-picked collections:
FAQs About the Chemical Formula of Epoxy
What is the chemical formula of epoxy resin?
“Epoxy resin” is a family of materials, so there is no single formula. The most common base resin is DGEBA, also called BADGE, with the molecular formula C21H24O4 for its neat monomer. Makers then blend it with curing agents to form the final plastic. DGEBA is widely used in coatings, adhesives, and composites.
What makes epoxy strong?
Epoxy resin hardens when its epoxide groups react with a curing agent to form a dense, cross-linked network. This tight network resists heat, impact, and many chemicals, which is why epoxy bonds and coatings last long. Higher cross-link density usually means higher stiffness and strength. Always follow the maker’s mix ratio to reach full properties.
Are all epoxies made from BPA?
No. Many epoxies are based on BPA, but there are BPA-free systems that use other phenols or bio-based building blocks. These are chosen for food contact, clear craft work, or regulatory needs. Always check the product’s technical sheet if you need BPA-free resin.
Why should craft makers care about epoxy chemistry?
Knowing the basics explains why exact mix ratios matter and why cure time and heat change with hardener type. It also helps you choose the right resin for clarity, working time, and final strength. Good chemistry habits reduce failed casts and sticky surfaces. Read the datasheet for mix by weight, pot life, and cure schedule.
Is epoxy safe after curing?
Properly mixed and fully cured epoxy becomes a hard, stable solid with very low emissions in normal use. The main risks are during mixing, pouring, and sanding, especially before full cure. Avoid breathing sanding dust and give the piece enough time to reach full cure per the maker’s guide. Use gloves, eye protection, and good ventilation for safe results.















Lämna en kommentar
Denna webbplats är skyddad av hCaptcha och hCaptchas integritetspolicy . Användarvillkor gäller.